A Very Short Introduction to Climate Change- M. Maslin
The PDF version of the book can be found here.
Chapter 1- What is global warming?

Chapter 4- Evidence for climate change
Chapter 1- What is global warming?
- What determines the earth's climate?
- Climate is controlled by 3 things: mass, distance from the sun, and composition of the atmosphere
- Humans have no control of the 1st 2, but it is by changing the 3rd that global warming is triggered
- How do we measure past climates?
- What is the IPCC?
- Intergovernmental panel on climate change
- There are 3 groups and a task force
- Write reports verified by 400 experts from 120 countries
- Compare the warming potential of different gases
- What are the different predictions for climate change?
- Global warming was ignored or refuted for a number of years, and it was only in the late 80's that international environmental awareness was discussed.
- the main reason people argued against it was because of problems with the data
- land monitoring was affected by the UHI
- method change for testing sea surface temperature
- as boats got bigger, more water evaporated when the bucket was hoisted up the side
- no explanation for the cooling of the 40-70s
- satellites came closer to earth due to friction with the atmosphere
- the models of the past don't match actual data
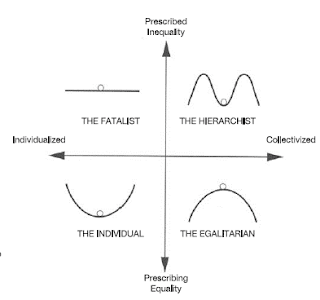
Chapter 3- Your viewpoint determines the future
These diagrams are very low quality, find them on page 41
These diagrams are very low quality, find them on page 41
- There are 4 ways to interpret how nature responds to change:
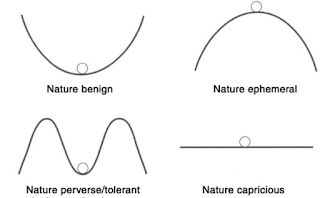
- Nature benign- robust, humans can't impact it
- Nature ephemeral- fragile, unforgiving to change
- Nature perverse- stable to a point of no return
- Nature capricious- unpredictable, out of human control
- How you perceive nature is linked to what you think will happen with global warming, and is based on your investments and upbringing


- Proxy variable - a measurable descriptor that stands in for the desired (but unobservable) variable
- Tempearature
- Tree ring thickness is a proxy variable- thicker rings show rapid growth in certain conditions, indicating a warmer climate
- Sea level
- Sea level is hard to measure because it is afftected by more than just climate e.g. isostatic rebound
- Permafrost
- When the climate is so cold, the top layer of the soil freezes
- The top metre is called the active layer
- it gets warm enough to melt
- the active layer is increasing
- Methane is released (positive feedback) and the ground becomes unstable and susceptible to avalanches
- Disproving sceptics:
- Sceptics: All of the data has been tweaked to find the desired trend
- Evidence: The data has to be adjusted to make it more accurate; however, even the raw data set shows the same trend
- Sceptics: Sunspot activity is responsible for climate change
- Evidence: To an extent, yes. But, it is not the sole cause
Chapter 6- What are the future impacts of global warming?
- Coastlines
- Rising sea levels result in shrinking and sinking coasts
- Storms/floods
- More heavy rainfall
- Bigger monsoons
- Continents are a lot warmer than the ocean in the summer
- less snow in Tibet increases continental temperatures further
- warmer climates mean the air can hold more water vapour
- There will be more variability- storms will be harder to predict
- there is no expected change with regards to hurricanes
- El Nino
- The southern oscillation is expected to be more frequent
- Bjorn Lomborg (The Skeptical Environmentalist)- global warming could turn off El Nino
- No evidence, but to be considered
- Health
- Less deaths as a result of the cold, but more due to overheating
- Water shortages
- Mosquitos
- Agriculture
- We don't yet know the impact of climate changes on food supply
- Increasing temperatures bring water shortages, pests, and crop failures
- But CO2 brings rapid growth and a quicker turnover
Chapter 7- Surprises
We assume global warming will be a linear increase, but we cannot know for certain- for instance, half of the total warming in Greenland occurred in 10 years
- Deep ocean circulation
- The Gulf Stream is responsible for moderating the climates of the USA, Europe, and West Africa
- Without it, our seasons would be extreme
- Gas hydrates
- Methane is trapped in ice lattices at the bottom of the ocean and under permafrost (high pressure, and low temperatures)
- If it melts, the methane is released in an explosion
- Submarine landslides = tsunamis
- Positive feedback, encouraging further climate change
- Isostatic rebound in Greenland and Antarctica is releasing the pressure needed to hold it in place
- The Amazon
- If the Amazon gets too dry, it will die forming a Savannah
- Savannahs hold less CO2, and are easily flammable
Chapter 8- Politics
There are a number of key players in discussions around climate change. Each group represents companies and countries- all of which have something to gain or lose from global warming.
- G77 + China
- Made of 77 developing countries
- Reducing emissions results in reducing development
- Carbon trading is positive, as it provides income
- AOSIS (Association of Small Island States)
- They want the tightest control on climate change as it will result in their extinction
- JUSCANZ [Also called the Umbrella Group)
- A group of developed countries
- Concerned with the cost of reduction and abatement
- A split in the group between oil dependent and eco-friendly countries.
- EU
- Work done should be in proportion to the level of development
- A very democratic and slow decision making body
- OPEC (oil exporters)
- Understand that by reducing global warming, they will lose business and act accordingly
Chapter 9- Alternatives
- Technofixes
- Removal of CO2 from industry
- Improve energy efficiency
- Renewable energy
- Afforestation
- Industrial uses of CO2
- Oil recovery
- Food manufacture
- Chemical manufacture
- Metal reprocessing
- Waste water processing
This was a VERY brief summary of some of the points I found most interesting, but the book gives a much more coherent and expansive explanation of the topics above.





Comments
Post a Comment